Table of contents
- Introduction to Fabric in Azure Data Factory
- Setting Up and Configuring a Fabric Workspace
- Working with Data Lakes and External Tools
- Running Pipelines and Understanding Performance
- Problem scenario
- Utilizing Spark Notebooks for Big Data
- Integration Possibilities with Snowflake and On-Premises Data
- Conclusion
- Source: Pragmatic Works [Link]
- Author: Dheeraj.Yss
- Connect with me:
Today, I am learning about Data Engineering in Microsoft Fabric.
Introduction to Fabric in Azure Data Factory
What is Microsoft Fabric?
Unified analytics fabric, End-to-end analytics data fabric, from the data lake to the business user.
What is data engineering?
Spark, Lakehouse, Pipelines, Dataflows Gen2.
Behind the scenes magic that makes all of the data work together its the process of designing & building and ultimately managing architecture of a data system including the structure and the organization.
orchestrating behind the scenes work, to ensure data is well prepared and is starring role in the analysis process involving different tasks like collecting & storing and also processing data so that it is easily accessible, usable downstream for consumption in Power BI reports.
Data engineers will setup the infrastructure that will create data pipelines, different tools for data transforms ensuring data is clean, organized and ready for analysis for business intelligence analyst.
Data integration work load inside fabric is going to provide data engineers with the ability to go through and unify by hybrid or multi cloud estates in an experience that combines the ease and use of power query editor in the power BI with the scale and power of data factory to be able to integrate and orchestrate all of data movement whether connected via on-premises in the cloud or third party sources.
Dataflow Gen2 - which essentially online power query editor inside power Bi service.
Lakehouse - store and access data.
spark - access data using python /SQL efficiently.
Lakehouse - like an Inner Join of Data warehouse (central repository for storing structured data forms from various sources for the purpose of business intelligence and reporting) along with a data lake (another repository to store different types of data whether it is structured so you can go through and store like tables and semi-structured with CSV files, parkuet files or unstructured data) so this lakehouse architecture allows you to store large amount data for an inexpensive bill Compare it to other sources.
In Lake House essentially, we are going to store Data on a data lake But having the structure of a traditional data warehouse Where you can go through and write SQL Operation against and have a confirmed acid properties Meaning that you have an ability to go in and make sure you Have the transactions and data Is going to be reliable.
What is datalake and onelake?
General purpose storage account
File formats: structured, semi-structured, un-structured)
containers / directories / sub-directories.
Datalake is like an onedrive for storing and accessing data in a single location so that all the different jobs that are going to be executed on a single source of truth.
Microsoft fabric one lake allows you to go through and store one copy of organizational data inside of a storage account which is like onedrive but for access inside of power BI service.
Importance of Compute in Fabric
Setting Up and Configuring a Fabric Workspace
switch to data engineering persona and select workspace.
Working with Data Lakes and External Tools
Provision a Lakehouse and name it. - essentially you are creating a container inside a storage account or a folder inside a storage account.
Note: Go through and store data inside fabric ultimately its going to be stored on onelake the dataklake thats managed by microsoft in your Fabric environment.
Note: Onelake - its a managed datalake inside of microsoft fabric you are provisioned with storage account.
shortcut: Integrate your other door data storage solutions Inside your Microsoft Fabric Lake House. Shortcut enables a data engineer to unify data across Clouds and accounts into your Microsoft fabric Lake House. Access files that resides in an external lake.
Right click Files / Create new shortcut / select Azure Datalake storage Gen2 / provide credentials (Can be found in the files provided link) & select Authentication kind: SAS Shared access signature/ Provide shortcut name: External data lake/ Subpath: / worldwide or simply checkbox worldwide / create.
Image:

Running Pipelines and Understanding Performance
Data factory pipeline activities:
Data movement, data transformation, control flow.
This pipeline will grab data from the fact table inside of the datalake shortcut created.
workspace / Create pipeline / fact_sales - data factory pipeline experience.
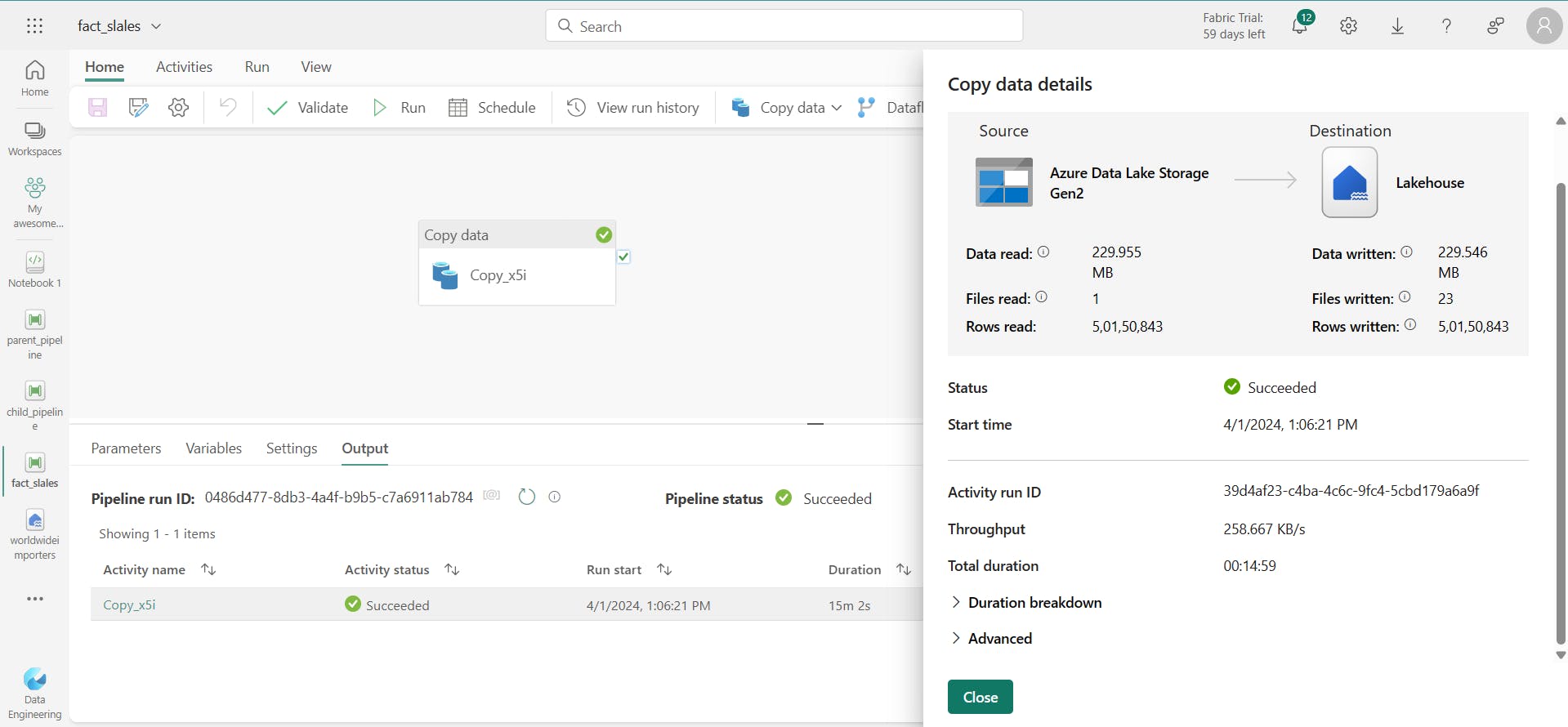
using copy assistant:
copy data/ copy assistant / azure data lake Gen2 / select Existing connection or create new connection/ test the connection / Choose the folder and the specific file: fact sales / next / Data destination: (We're pulling the data from data lake and where we need the data to be sent to. Hence, data destination, We are going to put this data in the Lake House) / choose lakehouse / next / select lakehouse / next / Select and map Folder path or table. / next /
Note: Parquet file - Low storage footprint, Column compressed.
Image:
Now,
using copy canvas:
create another pipeline: child_pipeline / copy data / add to canvas / source / data store type: external / select connection / test connection / browse / choose file: city / change file format to parquet / destination / Workspace/ Lake House/ Select Lake House/ Table name: dim_ city/ Choose advanced/ select overwrite / run.
Image:
Problem scenario
What if 5 or 100 tables to build pipelines. So we are not going to build pipelines for every single table instead we dynamically create pipelines to crete a metadata driven pipelines so we can extract info about data and use it along side of pipeline orchestration.
child_pipeline / parameters / file name, string, place holder. / click on copy data activity / Mapping the parameter to the mysource and my destination. / source / file path / add dynamic content / Launches pipeline Expression builder: select the parameter / ok / destination / table name: click x / add dynamic content / Launches pipeline Expression builder: add the code / ok / save child_pipeline.
This code replaces '.snappy.parquet' with '' (no space, just nothing)
@replace(pipeline().parameters.file_name,'.snappy.parquet','')
workspace / another pipeline: parent_pipeline / activities / get metadata (Returns information about names And data types About the files on data lake) / Settings / choose external data store type choose the connection / Browse / choose only the folder do not click on the file / ok / Add new field list (What are the different things that I want to return about this folder) / Select child argument (Essentially says What are the files that exist inside this folder) / home / run / Upset the output of the metadata /
Now lets filter the activity to exclude certain files inside the folder / elipses button to select filet activity / Create dependency or Precedence constraint from the get metadata activity by dragging the green cheque mark and hitting the filter activity / Settings/ items : add dynamic content / Launches pipeline Expression builder: Choose: child items / ok / condition / add the below code: / ok
@not(contains(item().name, 'fact'))
save and run the parent_pipeline / Observe the output.
Now,
to push the data into the lakehouse.
activities / for each / connect filter activity to foreach / items: add dynamic content / Launches pipeline Expression builder: Choose filter output, add the below code / ok
@activity('Filter1').output.value
edit for each activity / add invoke pipeline activity / settings / Select child pipeline/ value / add dynamic content / Launches pipeline Expression builder: Choose item & add the below code / ok
@item().name
go to main canvas / save and run.
go to lakehouse / refresh.
the duration of fact sales pipeline is 10 min and lets use spark notebook to better understand the file.
Utilizing Spark Notebooks for Big Data
to better understand a file.
workspace / new notebook / add Lakehouse to this notebook / add worldwideimporters lakehouse / add.
drop the fact sale file into note book / run.
df - dataframe.
Now,
count the records:
df.count()
50150843
now,
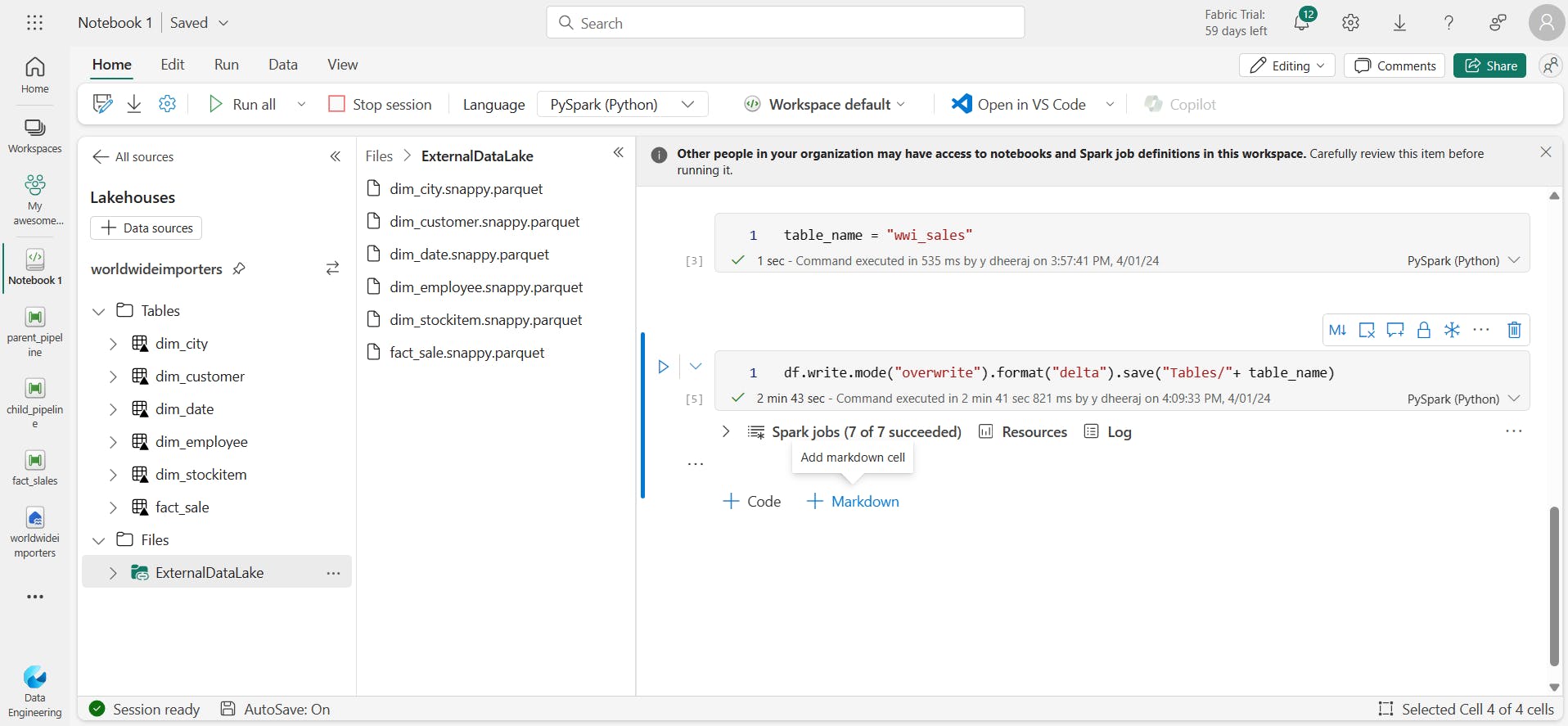
create table:
table_name = "wwi_sales"
code to bring data from datalake into lakehouse using spark by creating a table:
df.write.mode("overwrite").format("delta").save("Tables/"+ table_name)
Error:
An error occurred while calling o4367.save.
syntax error, fixed delt to delta.
Observed the duration 10 min took for pipeline to get data from shortcut into lakehouse and duration 3 min to bring data from datalake into lakehouse using spark.
Image:
creating temp viewfor the data that resides in df(dataframe) so that we can use other languages on this temp view:
df.createorReplaceTempview("fact")
Now to use SQL,
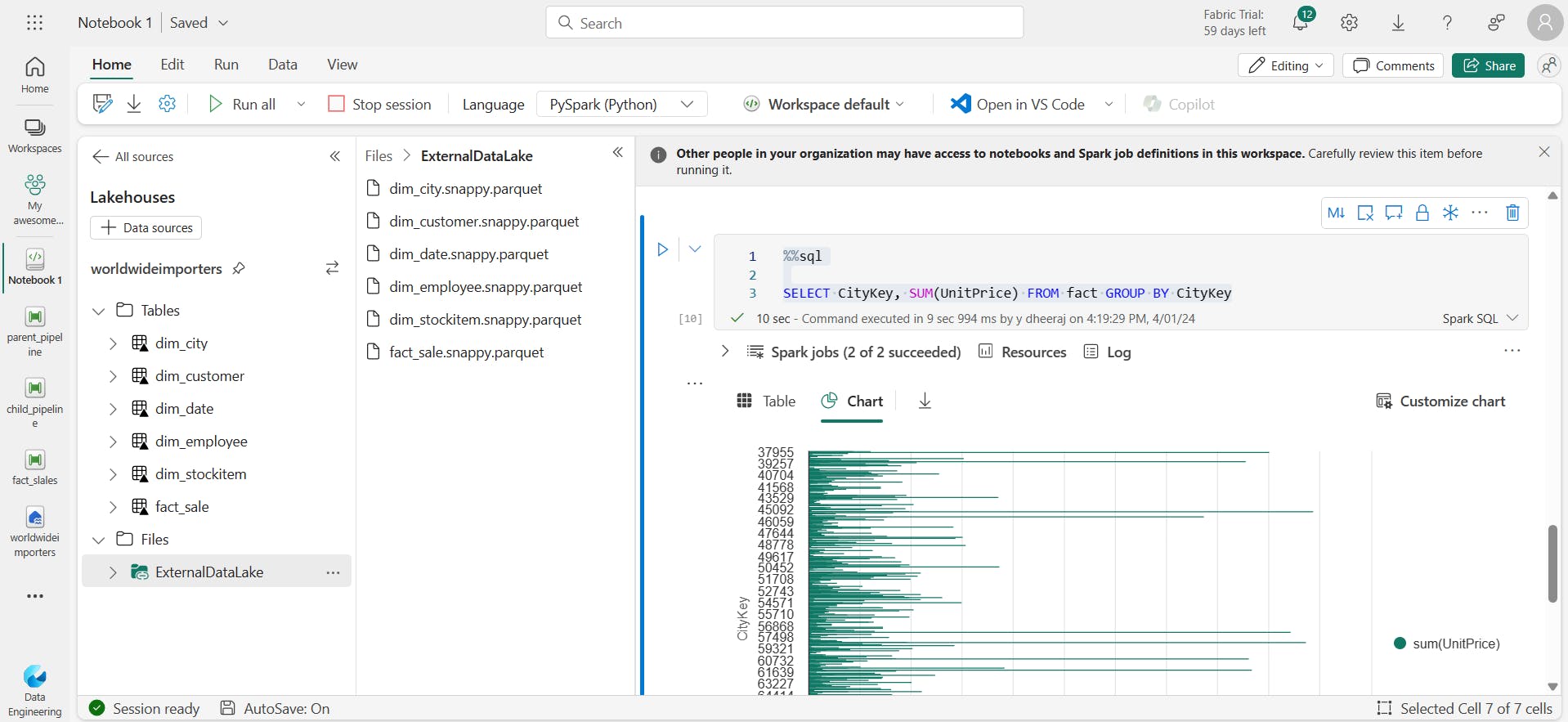
%%sql
Select * from fact
Performing aggregation:
%%sql
SELECT CityKey, SUM(UnitPrice) FROM fact GROUP BY CityKey
Image:
Integration Possibilities with Snowflake and On-Premises Data
You need a gateway.
Image:
Conclusion
Learning Objectives,
Introduction to Fabric in Azure Data Factory,
Microsoft Fabric, data engineering, Spark, Lakehouse, Pipelines, Dataflows Gen2, datalake and onelake, Spark Notebooks.
Creating pipelines and activities to read items in folders & dynamically run pipelines for items & also apply filters.
Observing duration between running a pipeline and spark while retrieving data from datalake into lakehouse.
Creating a table in lakehouse by pulling data from datalake using python spark notebook.