Today #Day99 of #100DaysOfCode, Learn JavaScript Array Reduce In 10 Minutes taught by WebDevSimplified.
1. syntax of reduce()
array.reduce((accumulator, currentValue) => { /* … */ })
providing initial value,
reduce((accumulator, currentValue, currentIndex, array) => { /* … */ }, initialValue)
2. What does reduce method in JS do?
reduce method() in JS reduces the array to one value.
The value can be anything like a number, object or string.
3. Example:
const array1 = [1, 2, 3, 4];
// 0 + 1 + 2 + 3 + 4
const initialValue = 0;
const sumWithInitial = array1.reduce(
(accumulator, currentValue) => accumulator + currentValue,
initialValue
);
console.log(sumWithInitial);
// Expected output: 10
4.Basics of reduce
Finding the total price,
I destructured the item for practice,
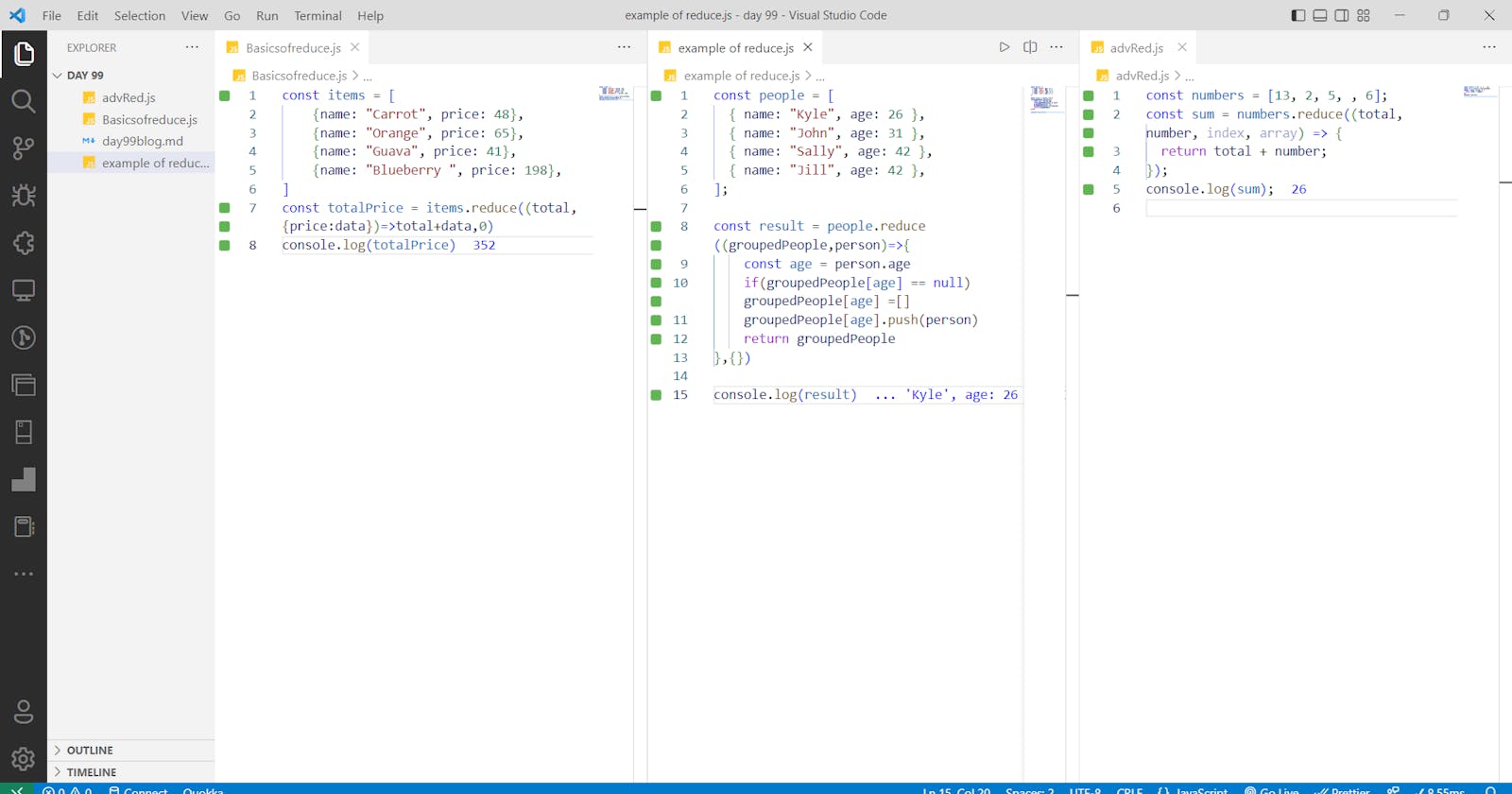
const items = [
{name: "Carrot", price: 48},
{name: "Orange", price: 65},
{name: "Guava", price: 41},
{name: "Blueberry ", price: 198},
]
const totalPrice = items.reduce((total,{price:data})=>total+data,0)
console.log(totalPrice)
Real world example of reduce
grouping people by age,
const people = [
{ name: "Kyle", age: 26 },
{ name: "John", age: 31 },
{ name: "Sally", age: 42 },
{ name: "Jill", age: 42 },
];
const result = people.reduce((groupedPeople,person)=>{
const age = person.age
if(groupedPeople[age] == null) groupedPeople[age] =[]
groupedPeople[age].push(person)
return groupedPeople
},{})
console.log(result)
advanced reduce feature
In the below we didn't pass the initial parameter,
total value is the numbers 0th index.
const numbers = [13,2,5]
const sum = numbers.reduce((total,number,index,array)=>{
return total+number
})
console.log(sum)
always mention the initialvalue as it will throw error when the array is a null,
const numbers = [13,2,5]
const sum = numbers.reduce((total,number,index,array)=>{
return total+number
},0)
console.log(sum)
Conclusion
I Learned about JavaScript Array Reduce and practiced reduce method.
Code
code