Today #day43 of #100daysofcode, I have completed 7.51 and 7.52 lessons and 'image slider' project code project in JS course. @Sololearn
7.52. event propagation
The HTML DOM supports two methods of event propagation: bubbling and capturing.
When an event occurs, the element order can be defined using event propagation. Which element's "click" event should be handled first if you have a
<p>element inside a<div>element and the user clicks on the<p>element?In bubbling, the event of the innermost element is handled first, followed by the event of the outermost element. The click event of the
<p>element is handled first, followed by the click event of the<div>element.When capturing, the event of the outermost element is handled first, followed by the event of the innermost element. The click event of the
<div>element is handled first, followed by the click event of the<p>element.
Note:
- Capturing goes down the DOM.
- Bubbling goes up the DOM.
1. Capturing vs. Bubbling
The addEventListener() method allows you to specify the propagation type with the "useCapture" parameter. Example:
addEventListener(event, function, useCapture)The default value is false, which means the bubbling propagation is used; when the value is set to true, the event uses the capturing propagation.
Example:
//Capturing propagation elem1.addEventListener("click", myFunction, true);//Bubbling propagation elem2.addEventListener("click", myFunction, false);This is particularly useful when you have the same event handled for multiple elements in the DOM hierarchy.
7.53. creating an image slider
1. Image Slider
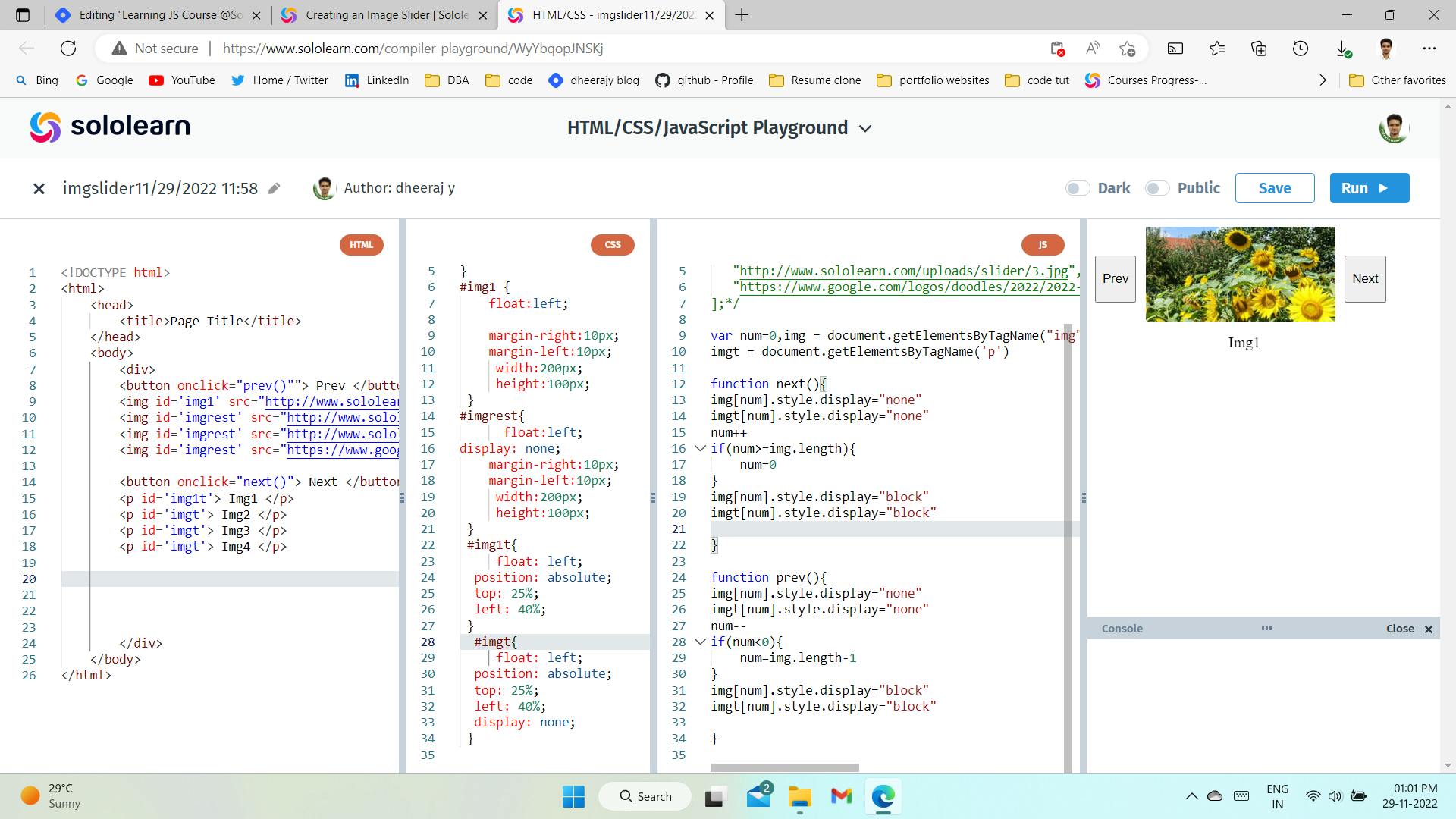
- Now we can create a sample image slider project. The images will be changed using "Next" and "Prev" buttons. Now, let’s create our HTML, which includes an image and the two navigation buttons:
2. code
- Image slider with title [click]
Images
- 7.51 & 7.52 completed
Conclusion
- event propagation
- Capturing vs. Bubbling
- Image Slider
- quiz
- Image slider code project
My Code:
- image slider project myowncode