Today #day47 of #100daysofcode, I have completed 8.58 & 8.59 and 2 code practice problems and 8.58.2 "Workout harder!" code problem in the JS course. @Sololearn
ECMAScript 6
1. ES6 Objects
- In ES6 there is a new shorthand notation in which you can declare a property as a function definition called a method without the function keyword in an object.
i. DATATYPES in JavaScript
- JavaScript has 2 types of DATATYPES
Primitive data types
string primitive data type,
number primitive data type, boolean primitive data type.
They are called primitive because they have no properties and method, I mean nothing is attached to them, it is just a plain number like 23 or a plain string like “hello” or a plain boolean like true or false.
Objects datatypes
While objects datatypes are array, regex, math, objects( there are also under objects datatypes), and many more. They are called objects datatypes simply because they have properties and methods. Objects are kings in javascript.
Example:
let man = {height: 6, colour: 'Brown', hands: 2, legs: 2}
In the above example, Man is an object, this object man has properties called 'height', 'color'; 'hands', 'and legs'.
Man is an object name, 'height', 'color', 'hands', 'and legs' are called property names of the object man.
The 6, 'brown', 2' and 2 respectively of 'height', 'color', 'hands', 'and legs' are called property values.
In JavaScript, we call these properties as keys and the property values as values in an object.
document.write(` the keys of the object man are ${Object.keys(man)}`)
document.write(` the key values of the object man are ${Object.values(man)}`)
document.write(`1. data type of ${man.height} = ${typeof(man.height)}`);
document.write(`2. data type of ${man.colour} = ${typeof(man.colour)}`);
Code: ES6OBJ [click]
Note:
Duplicate property names generated a SyntaxError in ES5 when using strict mode. However, ES6 removed this limitation.
ii. Computed Property Names
With ES6, you can now use computed property names.
Using the square bracket notation [], we can use an expression for a property name, including concatenating strings.
This can be useful in cases where we want to create certain objects based on user data (e.g. id, email, and so on).
Code: computedpropertyname [Click]
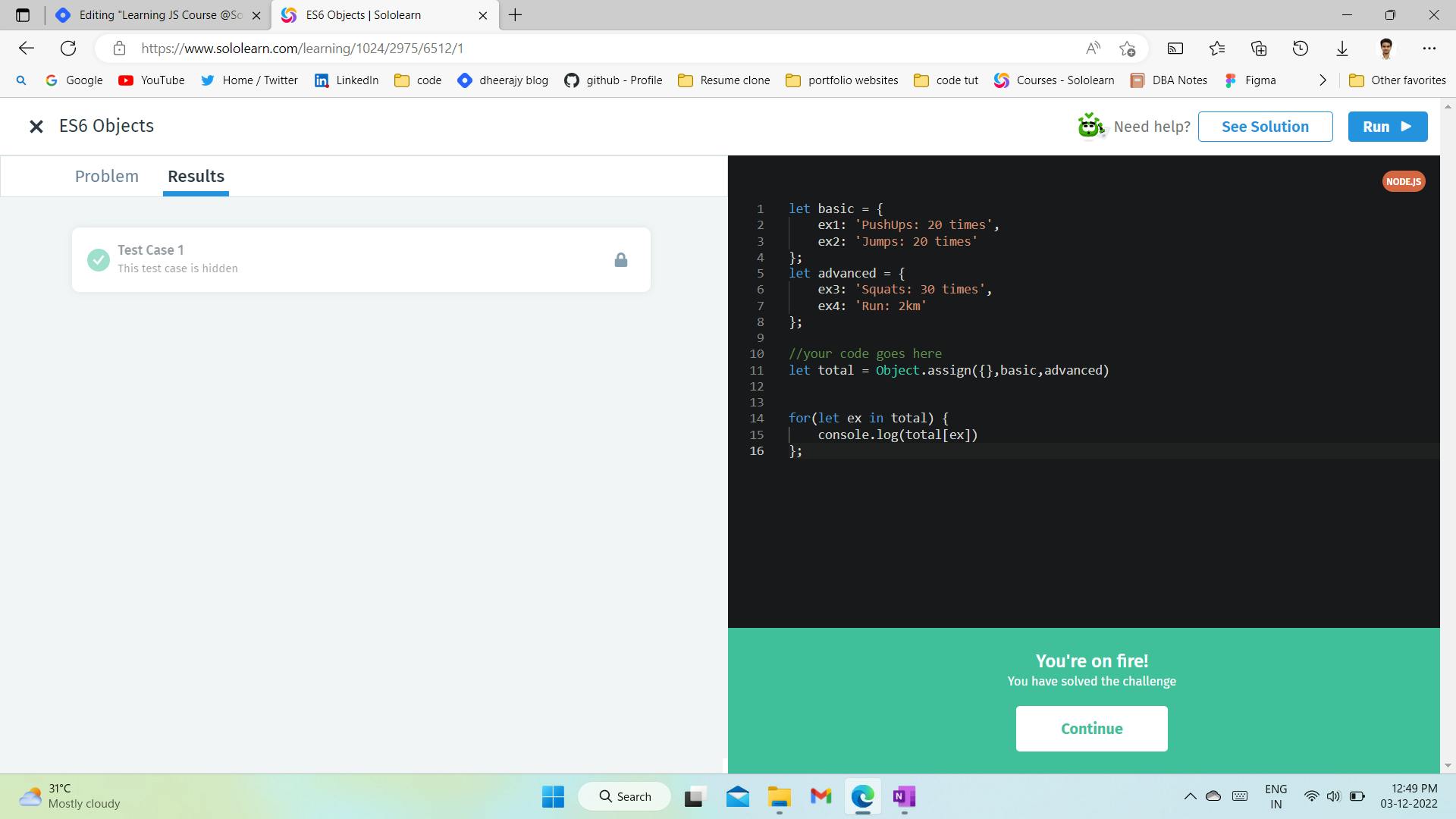
iii. Object.assign() in ES6
ES6 adds a new Object method assign() that allows us to combine multiple sources into one target to create a single new object.
Object.assign() is also useful for creating a duplicate of an existing object.
Example:
let person = {
name: 'Jack',
age: 18,
sex: 'male'
};
let student = {
name: 'Bob',
age: 20,
xp: '2'
};
let newStudent = Object.assign({}, person, student);
console.log(newStudent.name); // Bob
console.log(newStudent.age); // 20
console.log(newStudent.sex); // male
console.log(newStudent.xp); // 2
In Object.assign(), where the first parameter is the target object {} to which you want to apply new properties.
Each parameter following the first will be used as a source for the target. There are no restrictions on the number of source parameters that can be used.
Order is important, though, because properties in the second parameter will be overridden by properties with the same name in the third parameter, and so on.
In the preceding example, we used a new object as the target and two objects as sources.
Now, let's create a duplicate of the object person called dupperson object.
let dupperson = Object.assign({}, person);
Now, let's create a duplicate of the object person called dupperson object and then assigned a key value.
let dupperson = Object.assign({}, person, {name:'joey'});
In the above example, the target object{} the key name will be joey because in the second parameter Key name and its value Bob is being overwritten or overridden by the 3rd parameter in the object.assign{} which is name: 'joey'.
2. ES6 Destructuring
i. Array Destructuring in ES6
The destructuring assignment syntax is a JavaScript expression that makes it possible to unpack values from arrays, or properties from objects, into distinct variables.
ES6 has added a shorthand syntax for destructuring an array.
let array = [1,2,3]
let [one,two,three]=array
console.log(one) //1
In the above example, we have destructured the array value 1 and assigned it to the 'one' variable.
Now, let's destructure an array returned by a function,
let array = () =>{
return [1,9,7]
}
let [one,,three]= array()
console.log(three) //7
The destructuring assignment syntax will allow us to swap values simplified manner.
let x , y = 4 , z = 9, u = 32
[x,y=4] = [78] // x = 78 , y = 4
[y,z] = [z,y]
ii. Object Destructuring in ES6
In the same way as Array destructuring, Object destructuring unpacks properties into distinct variables.
let man = {name:joey,height:6}
let {n,h} = man
console.log(n) //joey
Now, let's assign without declaring the object man,
let man = {name:joey,height:6}
let n,h
( {n,h} = {name:'joey',height:6} )
console.log(n) //joey
() and ; are mandatory. Let's write a code where () is not required,
let {n,h} = {n:'joey',h:6}
We can also assign the object to new variable names.
let man = {name:joey,height:6}
let {n:nameofman,h:heightvalue} = man
//console.log(h); // Error, you cannot print the key
console.log(nameofman); //joey
You can assign default values to variables, in case the value unpacked from the object is undefined. Order is not important.
let man = {name:joey,height:6}
let {name:tony,hobby:playboy,height:5} = man
console.log(name); //tony
console.log(hobby); //playboy
Images
8.58 & 8.59 Lessons completed.
Conclusion
ES6 Objects
DATATYPES in JavaScript
Computed Property Names
Object.assign() in ES6
ES6 Destructuring
Array Destructuring in ES6
Object Destructuring in ES6
Quiz
Workout harder! code project