In this article, how to learn Fabric and power BI is presented.
Terms:
Persona: Your role. Data Analyst, Data Scientist.
This article focuses on the Power BI development persona.
Semantic Model: means data sets.
What is Microsoft Fabric?
All-In-One analytics solution for enterprises,
Offers a comprehensive suite of services,
Highly integrated, end-to-end, and easy-to use product.
In this article,
Navigating Fabric
Understanding OneLake Storage
Fabric Lakehouse
Building
Loading
SQL Endpoints
DirectLake
Microsoft has all the products with the right scale needed to build a complete analytics system.
Data integration + data engineering + data warehousing + real time analytics + Data science business intelligence ; Data Lake ; Governance and administration.
Different Workloads in Fabric:
Data Factory – The data integration Service
Analytic Workloads
Data Warehousing - Evolution of the existing SQL Pools,
Data Engineering – Spark Service for Data Transformations,
Data Science – A service to build, deploy, and manage ML Models,
Real-Time Analytics – An observational data analytics service collecting data from streaming sources,
Power BI – Business Intelligence Service.
Power BI Analyst
Lakehouse (As well associated dataset),
SQL Endpoint (Power Query Editor),
Power BI Reports,
Data Flows (Gen 2),
Data Pipeline.
I. Introduction to Lakehouse
OneDrive for data
It’s a data lake!
Supports Parquet/Delta/CSV/JSON
It’s all about Delta
One stop solution for structured and unstructured data.
Benefits and overview of One lake:
A single SaaS lake for the whole organization,
Provisioned automatically with the tenant,
All workloads automatically store their data in the OneLake workspace folders,
All the data is organized in an intuitive hierarchical namespace,
The data in OneLake is automatically indexed for discovery, MIP labels, lineage, PII, scans, sharing, governance and compliance.
We interact with one lake storage using Microsoft Fabric Lake House.
II. Data Lake, Data Set, and SQL Endpoint
What is a data lake?
General-purpose storage account
File Formats: (Structured, Semi-Structured, Unstructured)
Containers/Directories/Subdirectories
Data sets - Semantic Model.
SQL Endpoint - Query Tables, Manage Permissions, Create: Views, Table Valued Functions, Stored Procs.
III. Creating a workspace in Power BI for the Lakehouse
create a workspace and
create lakehouse
IV. Manual upload, data flows, and potential pipelines
Get Data/ upload files.
Manual upload:
Get data/ upload / choose files / upload / refresh
Previewing parquet Is currently not supported in one lake.
uploading a CSV file type - The datatypes are not recognized automatically. Later delete the table.
We use Spark to perform the datatype adjustments.
parquet file type - datatypes are recognized automatically. Highly compressed metadata rich file.
Now, drop the parquet file and observer the datatypes getting recognized automatically.
Now, upload adventure workbook.
Now, the new method Data flow Gen 2, a familiar tool power query will enable to connect to a data source and perform transform to solve the data types issues.
Dataflows Gen2,
Power Query Editor,
Data Destinations,
Integration Data Factory Pipelines.
DirectLake: Real time, Fast querying, No latency, No duplicate or copy of tables.
Get Data/ New Data flow Gen 2/ Get data / one lake hub / view more / choose the onelake / expand file / choose the files / create.
select CSV file in power Query / apply use first row as header - will automatically recognize the data types / choose the onelake destination - to load into lakehouse. / select gear icon / choose the lakehouse/ save settings/
select adventure file / duplicate / old adventure file / rename to customer / select customer / choose columns / choose the onelake destination - to load into lakehouse. / select gear icon / next /choose the lakehouse/ next/ save settings/
select duplicated adventure file / rename to date/ select date / choose columns / choose the onelake destination - to load into lakehouse. / select gear icon / next /choose the lakehouse/ next/ save settings/
change dataflow name to Load lakehouse / publish.
V. Using the SQL Endpoint for ad-hoc analysis and exploration
Go to workspace / select lakehouse type SQL analytics endpoint/
Visual queries is awesome.
VI. Creating relationships in the SQL Endpoint and how it impacts the Lakehouse
Select model to view relationships.
blue stripes is an indication that it is an direct lake connection.
Perform the relationships.
reporting tab/ automatically update semantic model.
create new mesure:
Total Sales = SUM(InternetSales_csv[SalesAmount])
VII. Comparison of connecting to the Lakehouse and the SQL Endpoint in Power BI
Connecting to Azure SQL Database for semanticmodel:
First create another new workspace and then create lakehouse and then create new data flow gen 2 with azure sql database option and provide credentials(given in the video comment link) then after getting all the tables, create new semantic model for the old work space so that semantic model will be copied to old work space.
Now, go to the AzureSQLdb Fabric DQ dataset semantic model / open data model / if you want to add mroe tables or establish relationships.
Connect to lakehouse in power BI:
Power BI / onelake datahub / power BI dataset / AzureSQLdb Fabric DQ dataset / start performance analyser /
Image showing DQ took more time:
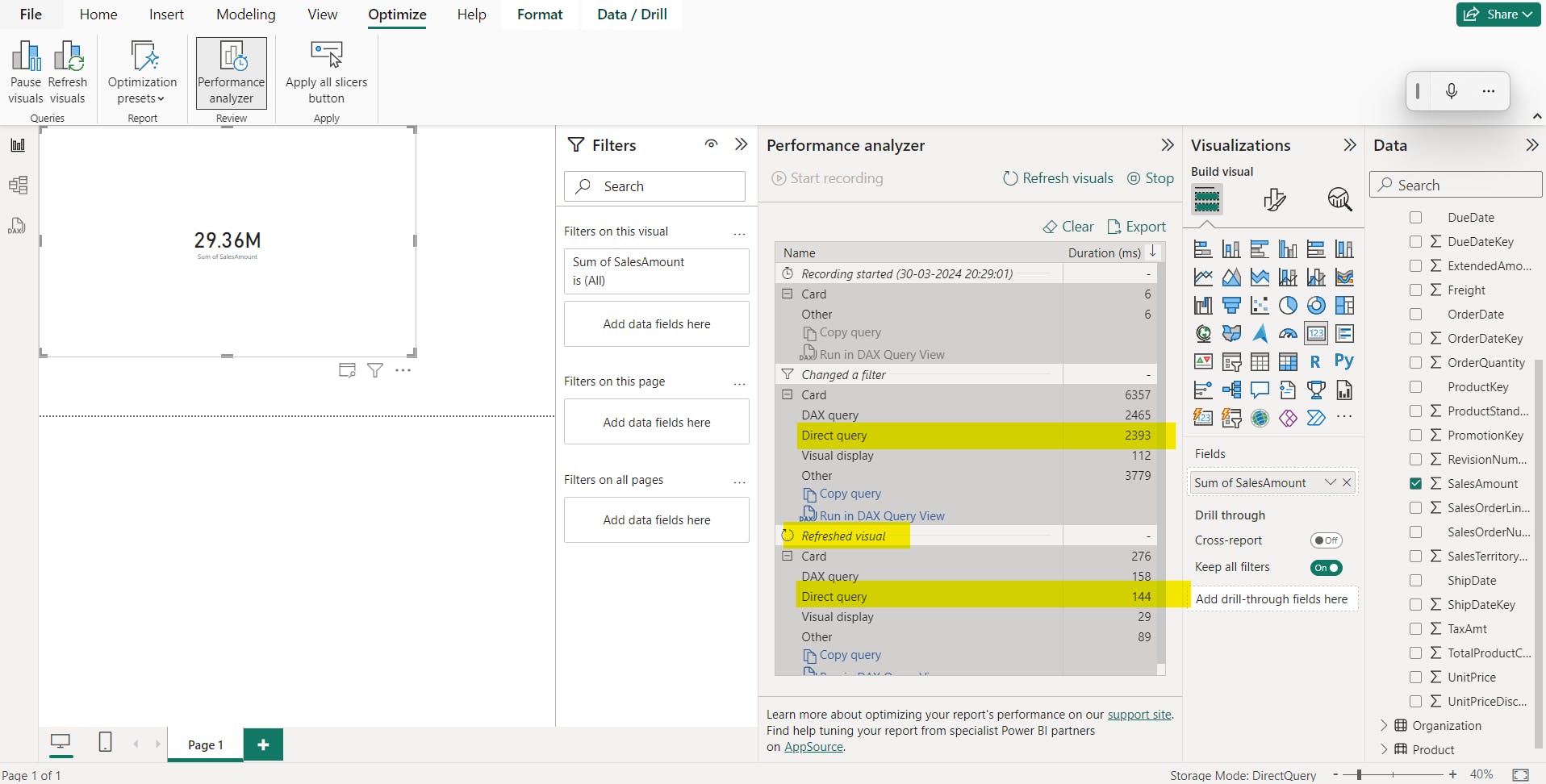
Now,
connecting to default dataset(semantic model) in power BI:
select lakehouse/
normal connect - not going to use direct query by default
connect to SQL end point - this won't show measures, you could use direct query option.
Image:
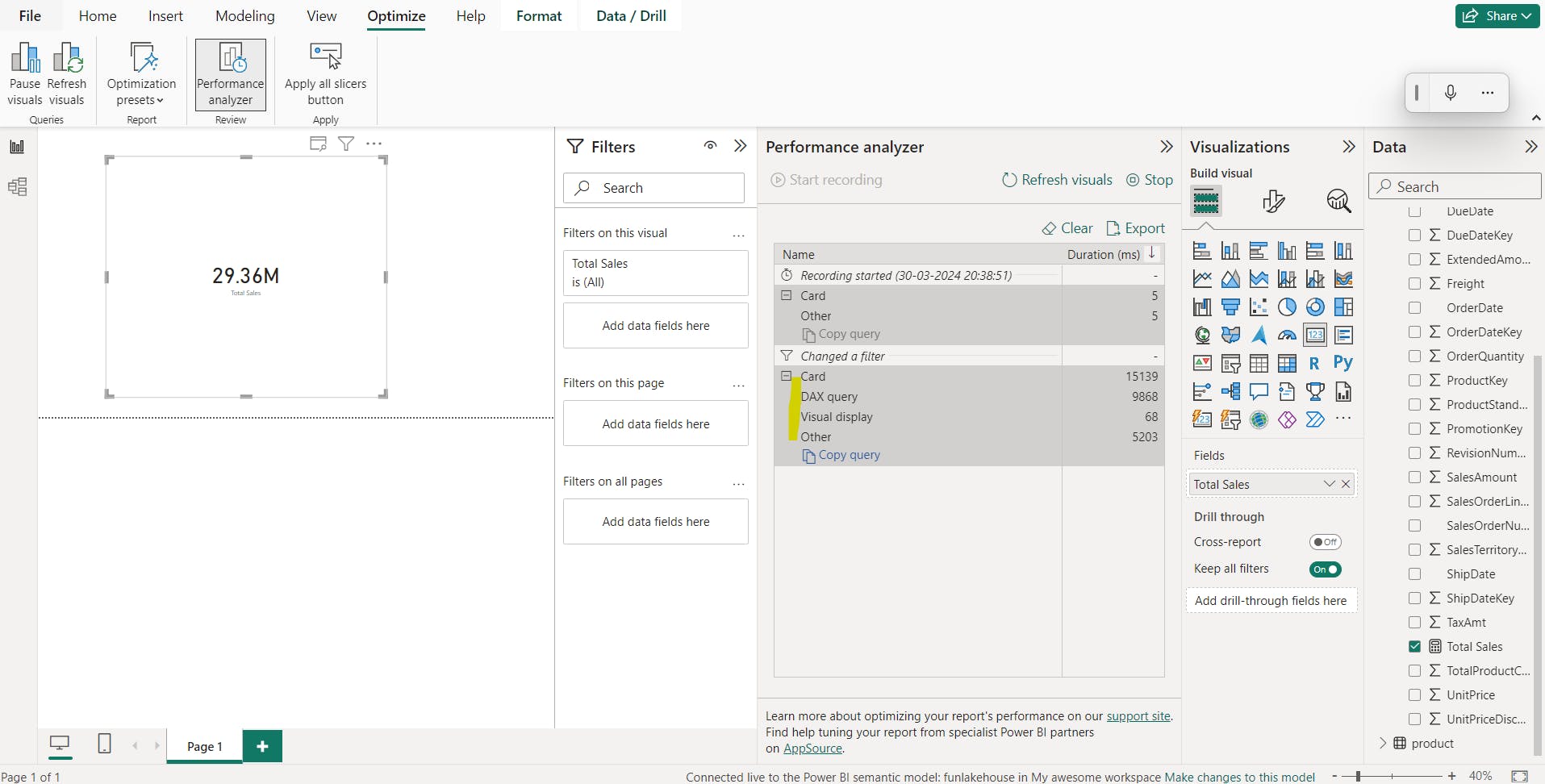
There will be a circumstance in which a scenario like performing complex tax queries or complex aggregations in these scenarios we will use direct queries.
VIII. Using pipelines for data engineering and its relevance to Power BI developers
Did not talked in the video.
Certification of completion:

Conclusion
Learning Objectives,
How we can take advantage of OneLake and Fabric Lakehouse to be our central storage location for housing our data to support your Power BI Reports.
Using manual upload or Using Dataflows Gen2 to continue taking advantage of the capabilities of Power Query to connect to data, transform it, and now load into the new Lakehouse.
Exploring your data stored in the Lakehouse either through the Power Query language or even using SQL.
How To Take advantage of the Lakehouse to use the new DirectLake connection to maximize the performance of your Power BI reports.