In this article, I am going to talk/practice about window functions. Rishabh Mishra YT has beautifully explained about Window functions.
Diagram
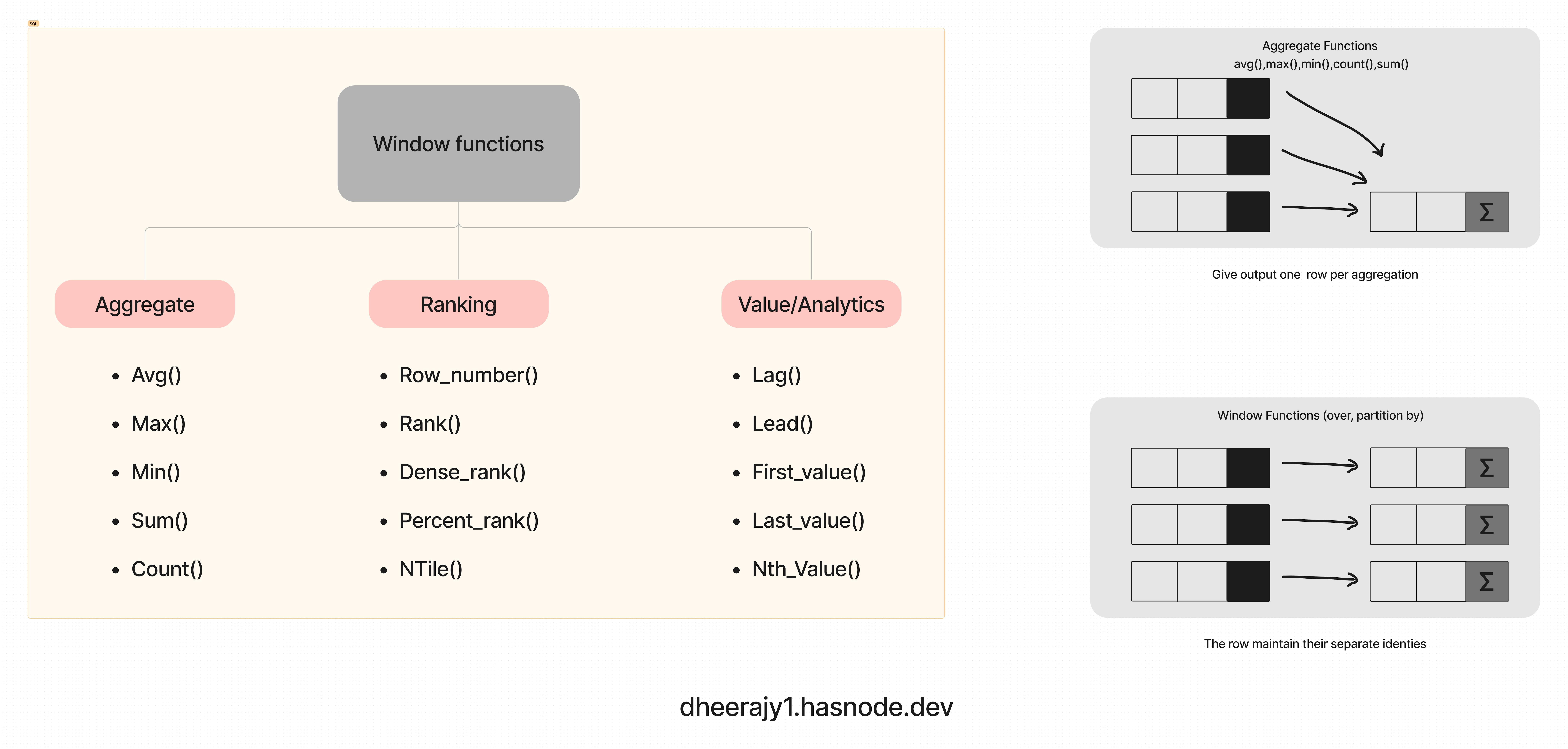
Window function
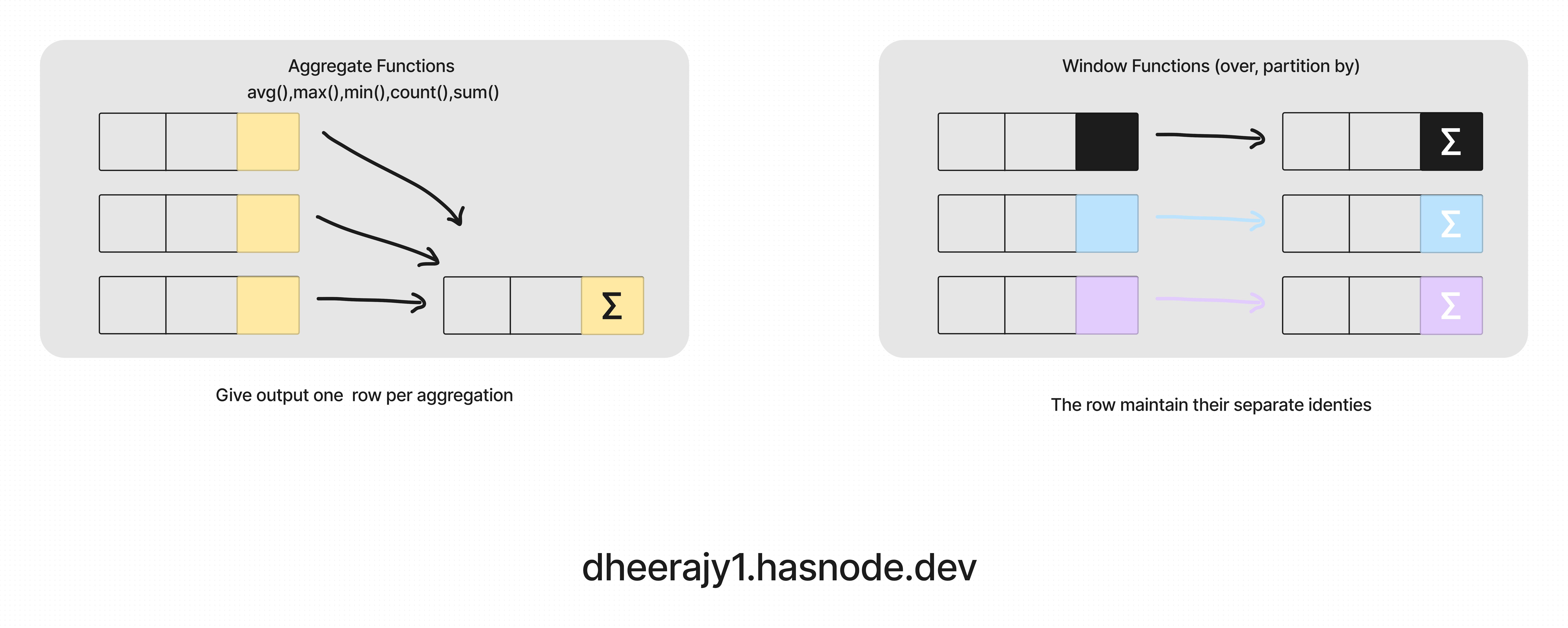
Window function applies aggregate, ranking & analytic functions over a particular window(set of rows).
Over clause is used with window functions to define that window.
Diagram
Window function syntax,
select column_names(s),
fun(expression) over ( [<partition by clause>]
[<order by clause>]
[<row or range clause>] )
from table_name
where fun() are aggregate fun or ranking fun or analytic fun
Define a window - partition by , - order by, rows
window function terms,
window function -- applies aggregate, ranking & analytic function over a particular window(or set of rows) for example sum(),avg(), row_number()
Expression -- is the name of the column that we want the window fun operate on. This may not be necessary depending on what function is used. like we pass a column name to a function
Over -- is just to signify this is a window function and also used to define the window
partition by -- divides the rows into partitions so we can specify which rows to use to compute the window function.
order by -- is used so that we can order the row within each partition,
rows -- can be used if we want to further limit the rows within a partition.
Data
Create table
create table test_data
(
new_id bigint,
new_cat varchar(20)
)
insert into
insert into test_data
values (100,'Agni'),
(200,'Agni'),
(200,'Vayu'),
(300,'Vayu'),
(500,'Vayu'),
(500,'Dharti'),
(700,'Dharti')
Window function example
I. Aggregate functions
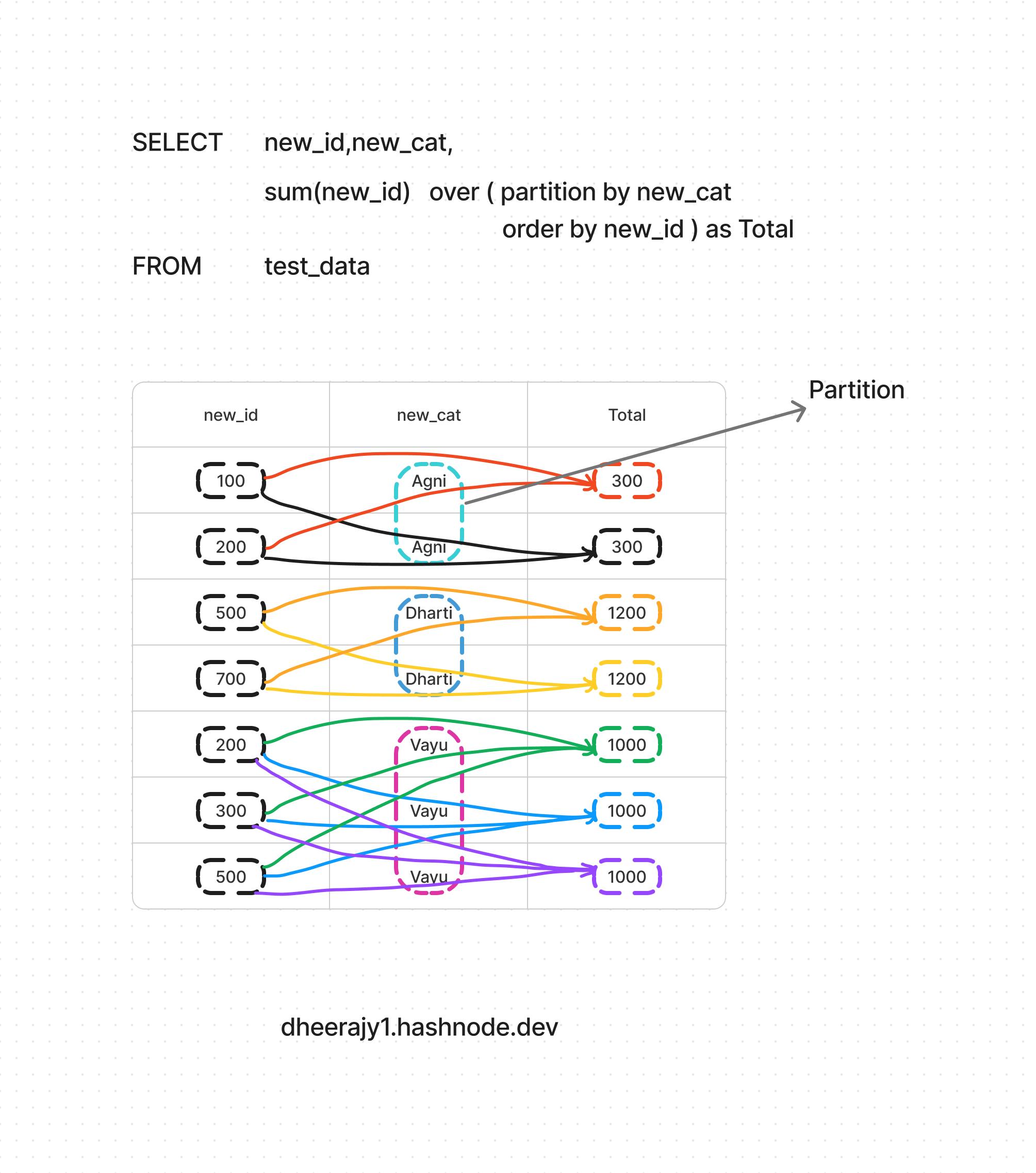
i. using aggregate sum() functions,
SELECT new_id,new_cat,
sum(new_id) over ( partition by new_cat
order by new_id ) as Total
FROM test_data
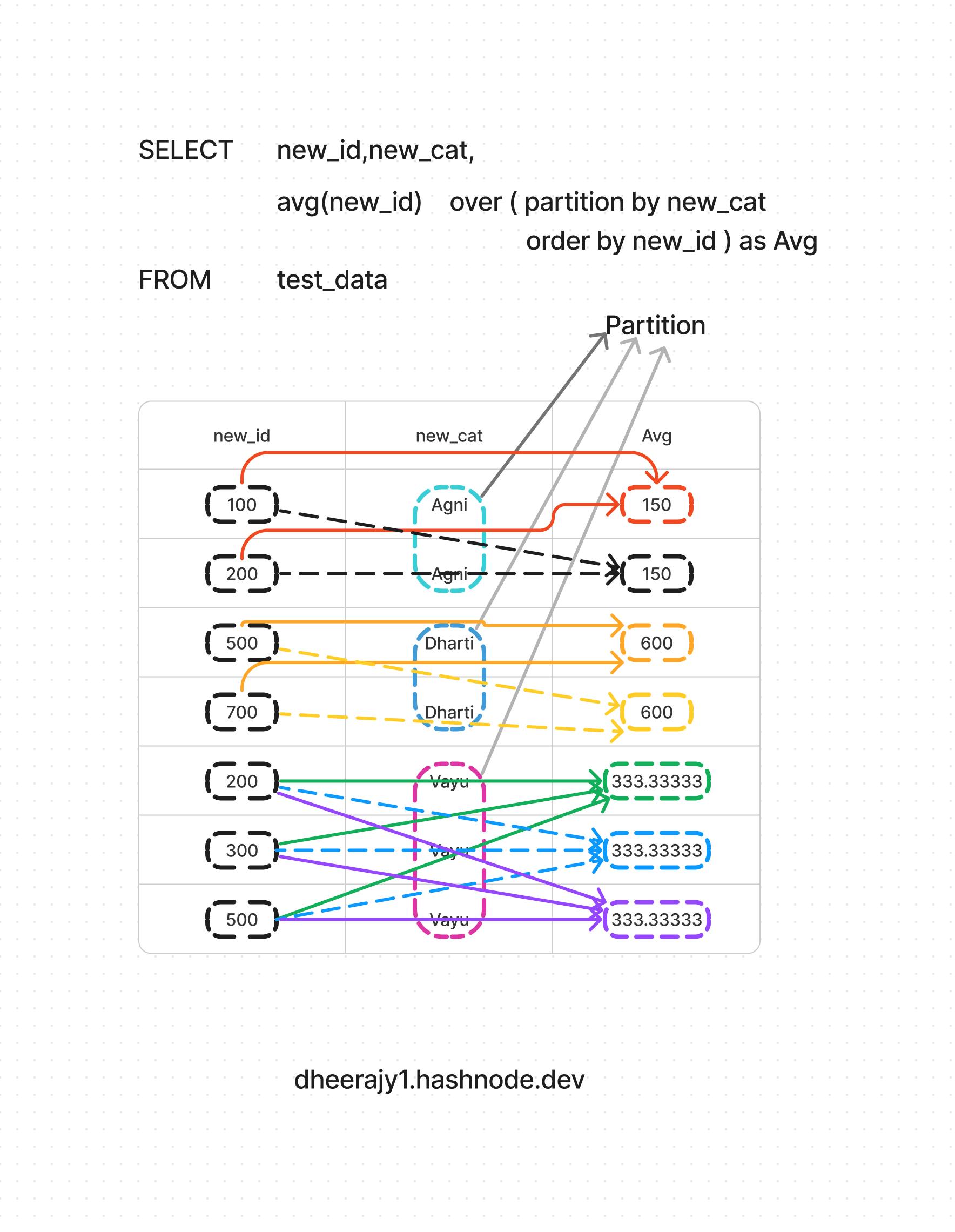
ii. using aggregate avg() functions,
SELECT new_id,new_cat,
avg(new_id) over ( partition by new_cat
order by new_id ) as Avg
FROM test_data
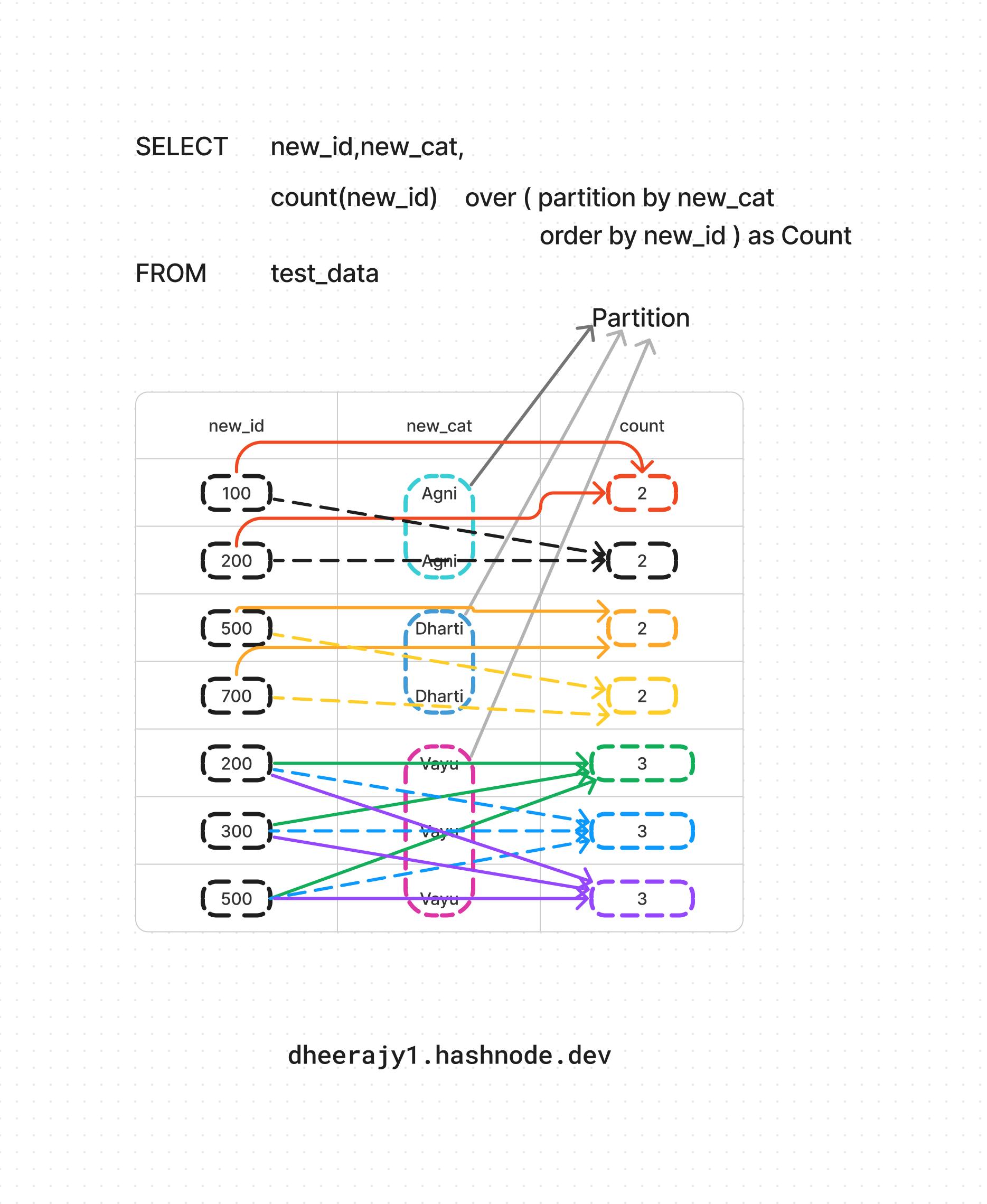
iii. using aggregate count() functions,
SELECT new_id,new_cat,
count(new_id) over ( partition by new_cat
order by new_id ) as Count
FROM test_data
iv. using aggregate min() functions,
SELECT new_id,new_cat,
min(new_id) over ( partition by new_cat
order by new_id ) as Min
FROM test_data

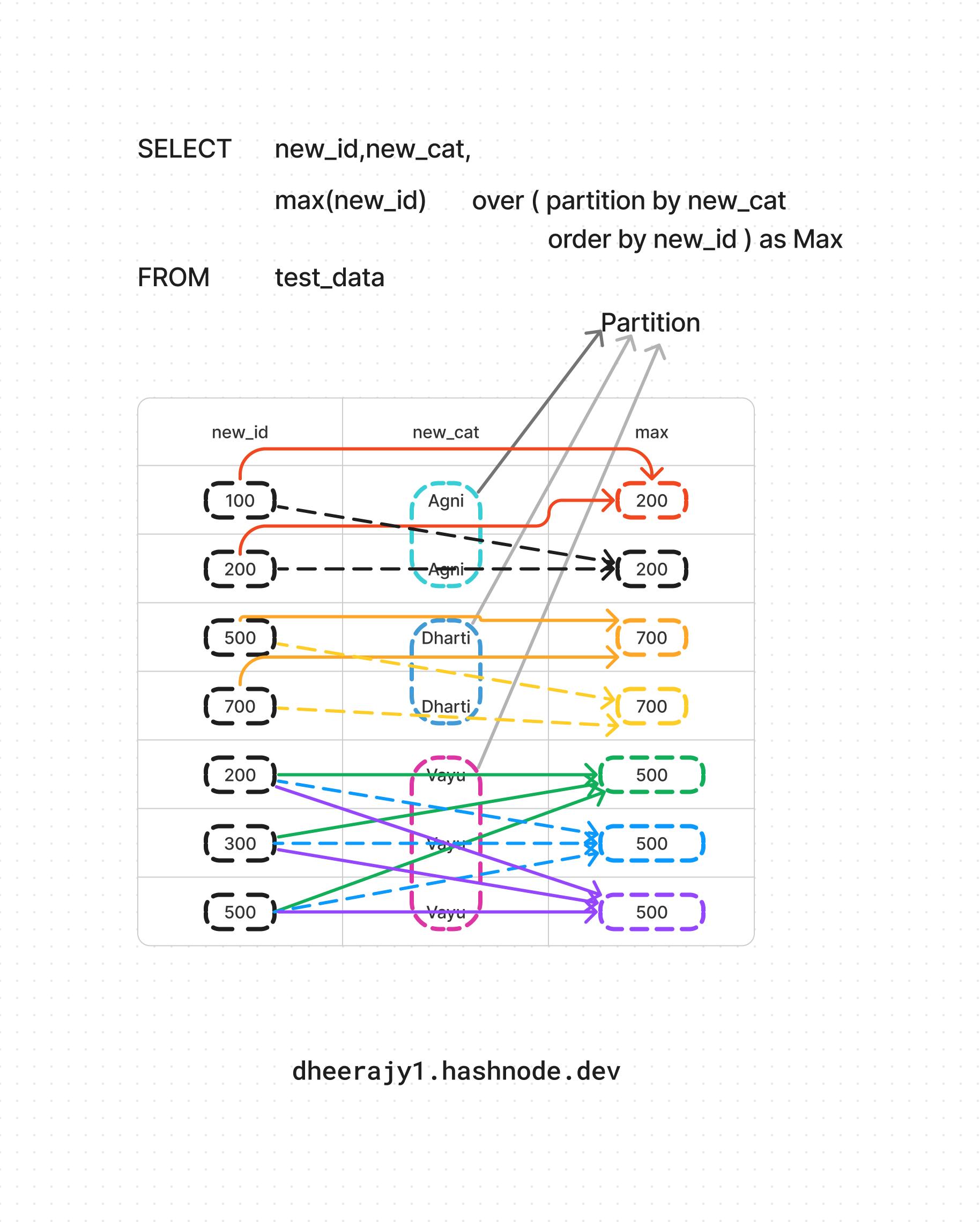
v. using aggregate max() functions,
SELECT new_id,new_cat,
Max(new_id) over ( partition by new_cat
order by new_id ) as Max
FROM test_data
vi. using rows/ range clause,
SELECT new_id,new_cat,
sum(new_id) over ( order by new_id
rows between unbounded preceding
and unbounded following ) as Total,
avg(new_id) over ( order by new_id
rows between unbounded preceding
and unbounded following ) as Avg,
count(new_id) over ( order by new_id
rows between unbounded preceding
and unbounded following ) as Count,
min(new_id) over ( order by new_id
rows between unbounded preceding
and unbounded following ) as Min,
max(new_id) over ( order by new_id
rows between unbounded preceding
and unbounded following ) as Max
FROM test_data
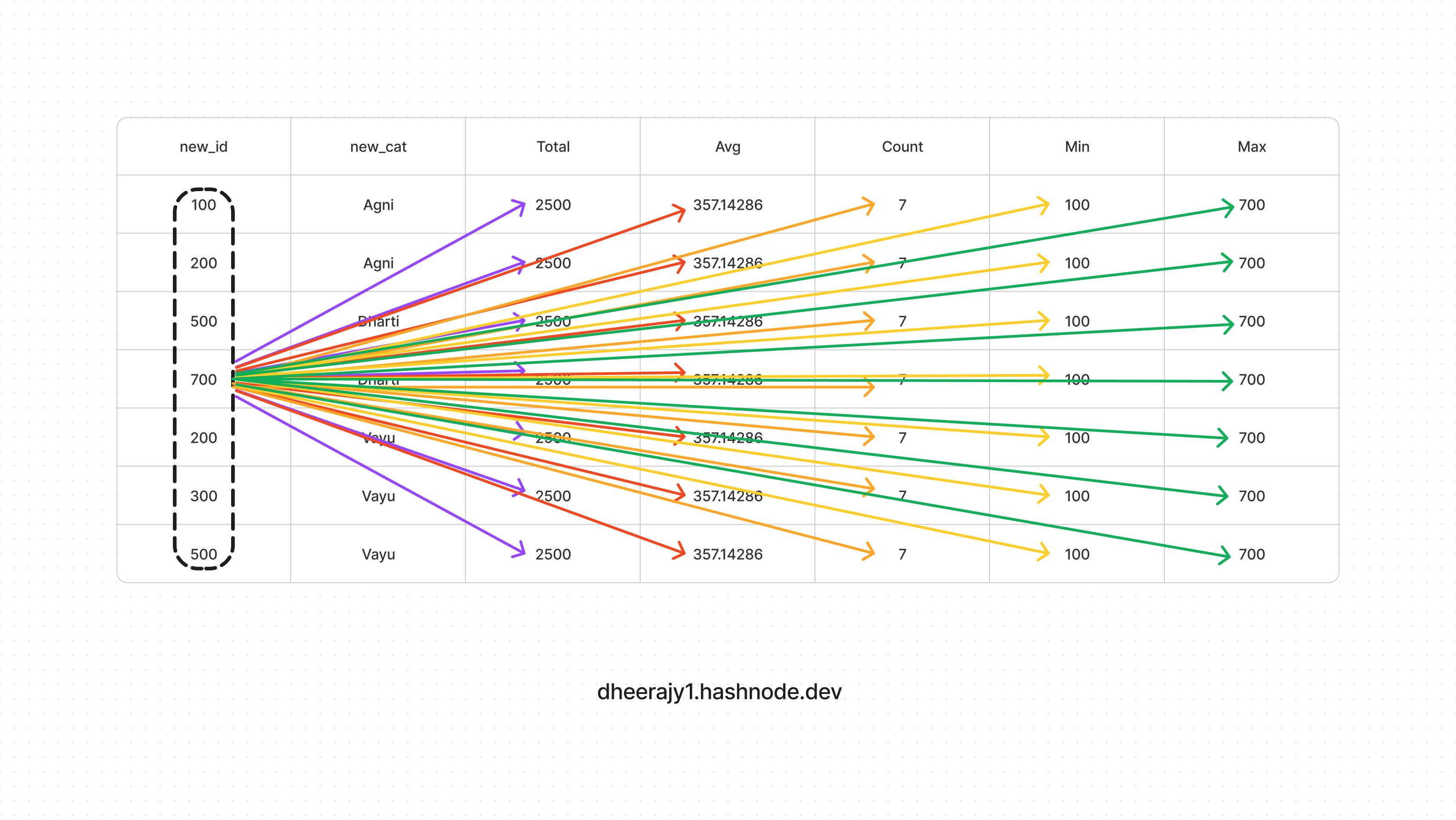
Note:
- Above used, 'rows between unbounded preceding and unbounded following' which will give a single output based on All input values/partition (if used)
Test cases
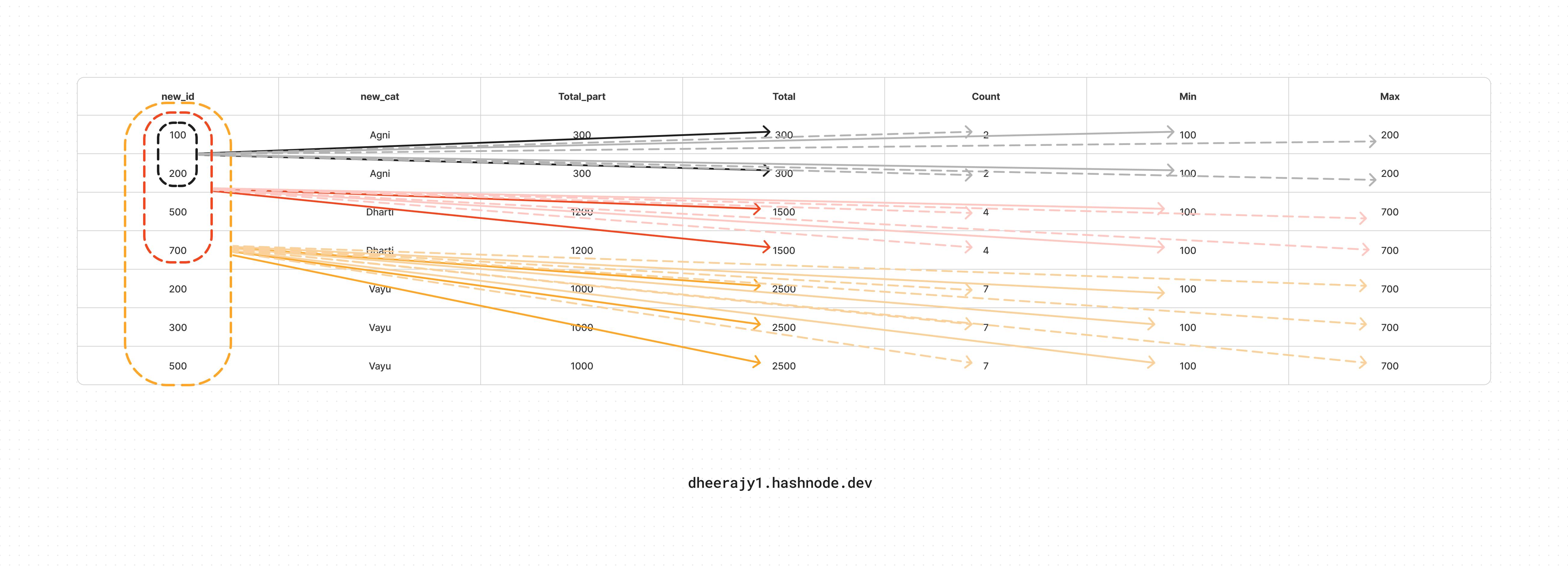
Test Case - 1: no partition, order by new_cat
select new_id, new_cat,
sum(new_id) over (partition by new_cat order by new_cat) as Total_part,
sum(new_id) over (order by new_cat) as Total,
count(new_id) over (order by new_cat) as Count,
min(new_id) over (order by new_cat) as Min,
max(new_id) over (order by new_cat) as Max
from test_data
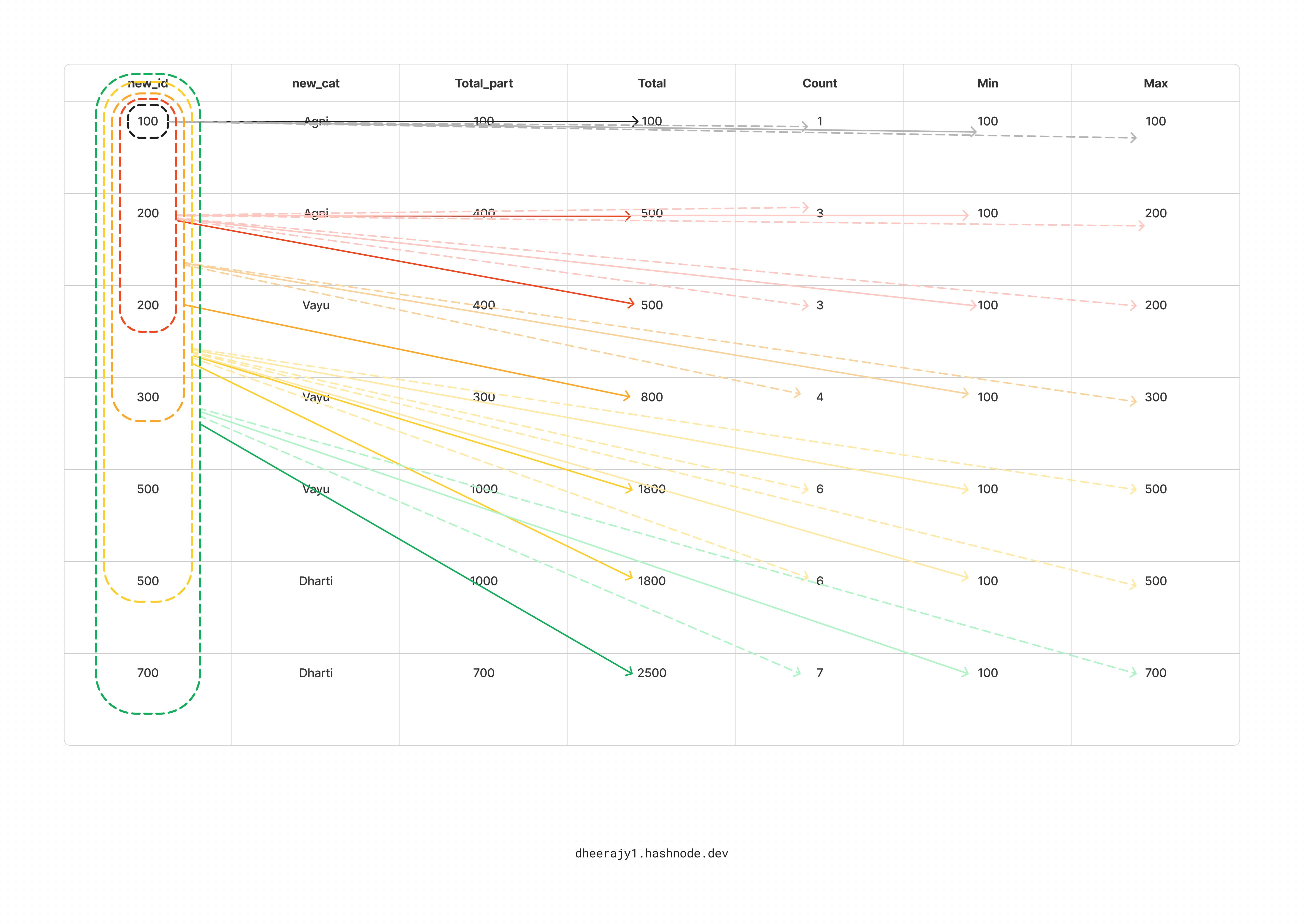
Test case -2: no partition, order by new_id
select new_id, new_cat,
sum(new_id) over (partition by new_id order by new_id) as Total_part,
sum(new_id) over (order by new_id) as Total,
count(new_id) over (order by new_id) as Count,
min(new_id) over (order by new_id) as Min,
max(new_id) over (order by new_id) as Max
from test_data
II. Ranking functions
i. using row_number() ranking function
SELECT new_id,
row_number() over(order by new_id) as Row_number
FROM test_data

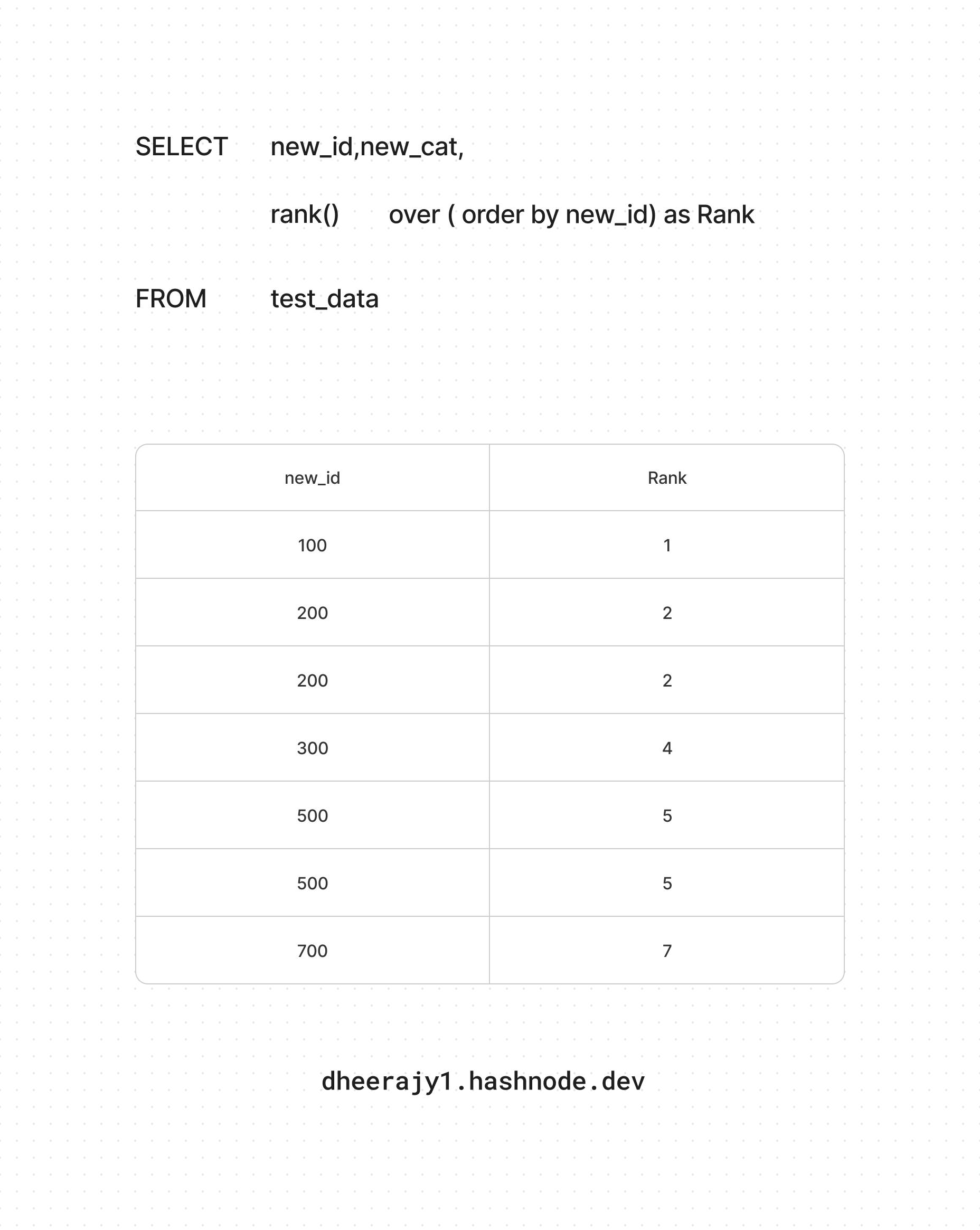
ii. using rank() ranking function
rank() ranking function :
unique value - unique rank
duplicate values - same rank
Yes skips rank
SELECT new_id,
rank() over(order by new_id) as Rank
FROM test_data
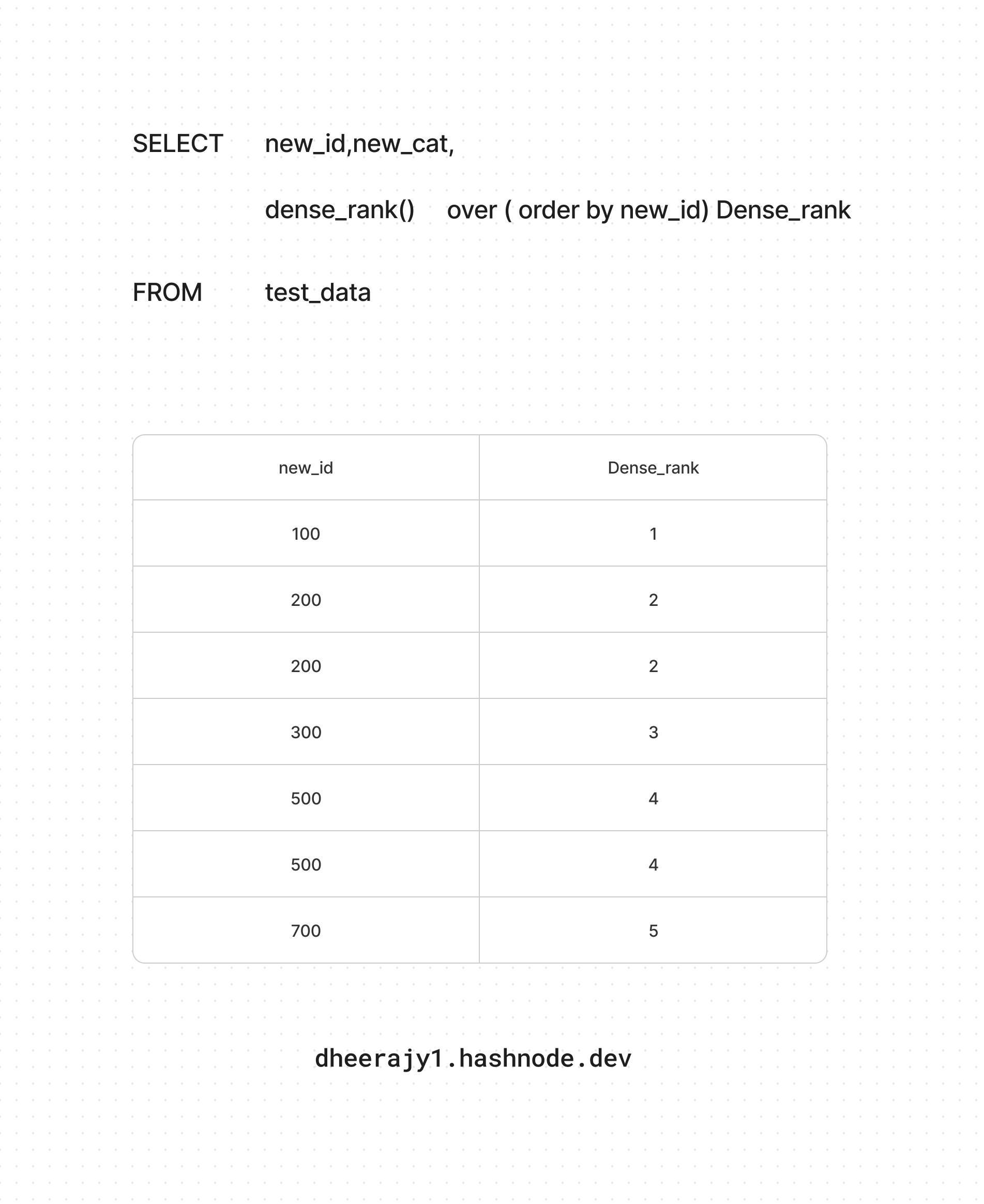
iii. using dense_rank() ranking function
dense_rank() ranking function:
unique value - unique dense_rank
duplicate values - same dense_rank
No skips rank
SELECT new_id,
dense_rank() over(order by new_id) as Dense_rank
FROM test_data
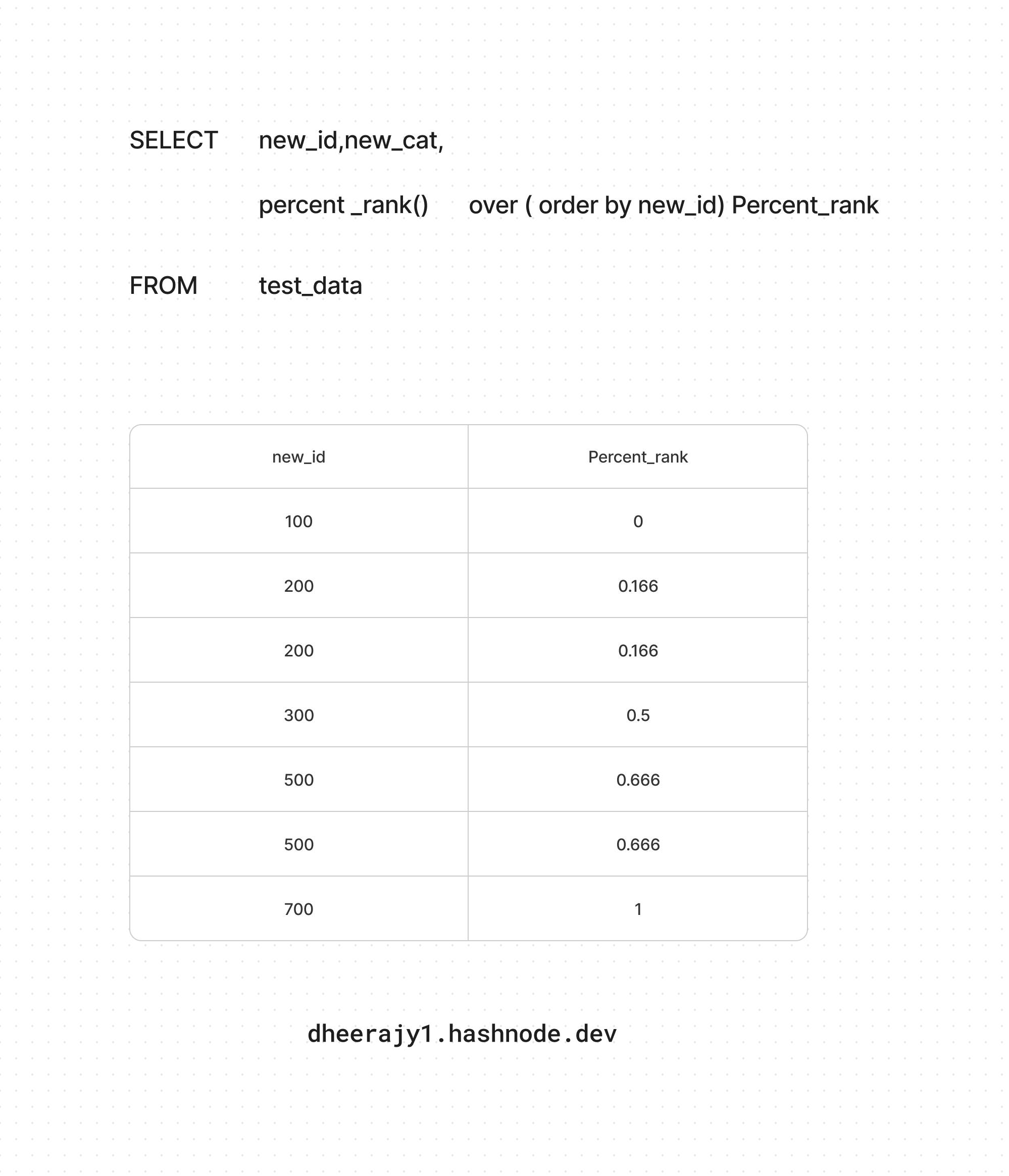
iv. using percent_rank() ranking function
SELECT new_id,
percent_rank() over(order by new_id) as Percent_rank
FROM test_data
III. Analytic/Value function
i. using first_value() Analytic/Value function
SELECT new_id,new_cat,
first_value(new_id) over ( order by new_id) as First_value
FROM test_data

ii. using last_value() Analytic/Value function
SELECT new_id,new_cat,
last_value(new_id) over ( order by new_id) as Last_value
FROM test_data

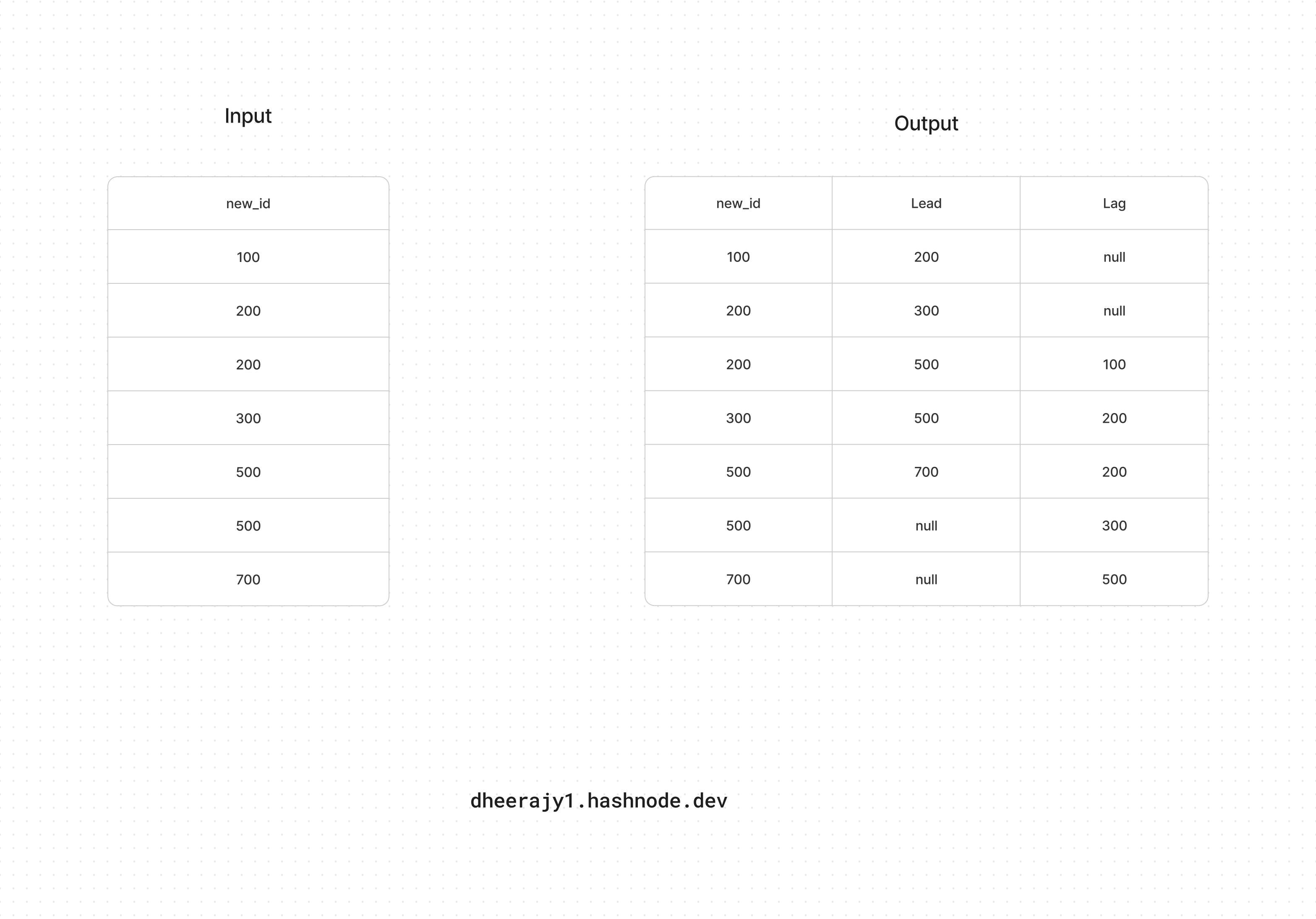
iii. using lead() Analytic/Value function
SELECT new_id,new_cat,
lead(new_id) over ( order by new_id) as Lead
FROM test_data

iv. using lag() Analytic/Value function
SELECT new_id,new_cat,
lag(new_id) over ( order by new_id) as Lag
FROM test_data

Window function Assignment
Offset the lead and lag values by 2 In the output columns.
Answer
SELECT new_id,new_cat,
lead(new_id,2) over ( order by new_id) as Lead,
lag(new_id,2) over ( order by new_id) as Lag
FROM test_data
Conclusion
Learning Objectives,
Definition of window function in SQL,
Syntax of window function,
Examples of window functions using aggregate functions,
Two Test Cases in aggregate window functions,
Examples of window functions using ranking functions
Examples of window functions using analytic/value functions